For example, while one type of absolute age dating may be perfect to figure out how old a dinosaur bone fossil is, another method of dating might be perfect to.
Table of contents
- Absolute dating
- Navigation menu
- Absolute Age: Definition & Dating
- Absolute Age: Definition & Dating | arraya.co
This can be useful in dating certain types of rocks because the last time they were heated is most likely when they were formed. In order to use this type of dating, the material must be heated to degrees Celsius and the resulting light is measured and analyzed. This is just a fancy term for counting tree rings! It is not an old myth that by counting the rings in the cross-section of a tree you can tell how old it is.
Scientists can take very accurate readings using this method, often to the exact calendar year. This method is useful when determining the age of a material that was once alive. All living things contain amino acids. By counting the amounts of certain amino acids, scientists can determine how long ago the specimen died. In absolute age dating, scientists determine the age of Earth materials as precisely as possible. Many scientists prefer the term calendar dating, as it implies that ages determined can be plotted on a calendar.
Absolute dating
There are many different types of absolute age dating methods because many different types of materials exist. Each material and situation has an optimal method that should be used in determining its age. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study. Login here for access. Did you know… We have over college courses that prepare you to earn credit by exam that is accepted by over 1, colleges and universities.
You can test out of the first two years of college and save thousands off your degree.
Navigation menu
Anyone can earn credit-by-exam regardless of age or education level. To learn more, visit our Earning Credit Page. Not sure what college you want to attend yet? The videos on Study. Students in online learning conditions performed better than those receiving face-to-face instruction. Explore over 4, video courses. Find a degree that fits your goals. Try it risk-free for 30 days. Add to Add to Add to. Want to watch this again later? Imagine braving the desert heat for days or even weeks as you dig for dinosaur bones.
You find something extraordinary and want to know as much about it as you can. In this lesson, you'll learn how scientists determine the absolute age of materials. What is Absolute Age? Try it risk-free No obligation, cancel anytime. Want to learn more? Select a subject to preview related courses: Lesson Summary In absolute age dating, scientists determine the age of Earth materials as precisely as possible. Register to view this lesson Are you a student or a teacher?
I am a student I am a teacher.
Unlock Your Education See for yourself why 30 million people use Study. Become a Member Already a member?
What teachers are saying about Study. Earning College Credit Did you know… We have over college courses that prepare you to earn credit by exam that is accepted by over 1, colleges and universities. To learn more, visit our Earning Credit Page Transferring credit to the school of your choice Not sure what college you want to attend yet? Browse Articles By Category Browse an area of study or degree level. You are viewing lesson Lesson 9 in chapter 17 of the course:. Help and Review 28 chapters lessons. Mineral Types, Properties, and Earth and Celestial Rocks: Igneous Rocks in Geology: Sedimentary Rocks in Geology: Metamorphic Rocks in Geology: Rock Deformation, Geological Folds Running Water in Geology: Ground Water in Geology: Water Balance in Geology: Plate Tectonics in Geology: Energy Resources in Geology: This is done by multiplying the number of half-lives that have passed by the half-life decay constant of the parent atom again, this value is determined in a laboratory.
To summarize, the key piece of information that needs to be determined from a mineral specimen in order to determine its absolute age is its age in number of half lives.
This can be mathematically determined by solving for y in this equation:. Let's work through a hypothetical example problem. Suppose you analyzed a mineral sample and found that it contained 33, parent atoms and 14, daughter atoms. Further, suppose that the half-life of the parent atom is 2. How old is the mineral sample?
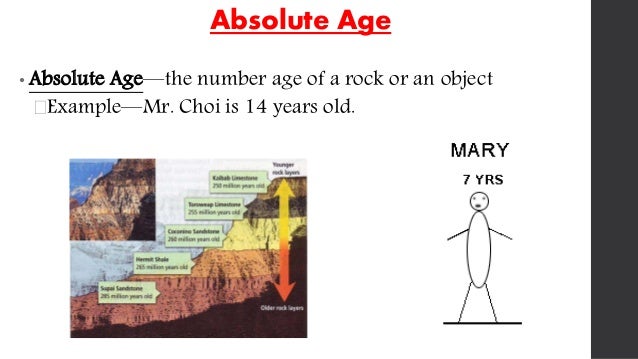
Absolute Age: Definition & Dating
First, we know that: So, we conclude that 0. As noted above, a radiometric date tells us when a system became closed, for example when a mineral containing radioactive parent elements first crystalized. An individual mineral grain may have a long history after it first forms. For example, it may erode out of an igneous rock and then be transported long distances and over long periods of time before it is finally deposited, becoming one grain among billions in a layer of sedimentary rock e.
- bsa frame number dating!
- friday night speed dating london!
- dating mumbai india!
- dating texas cowboys!
- great online dating profiles for women examples!
Further, heating mineral grains to great temperatures can cause them to leak parent and daughter material, resetting their radiometric clocks. The melting involved with metamorphic change can reset the radiometric clock. For example, suppose an igneous rock formed 2. If it were subjected to metamorphism 1. As noted above, the rate at which a given radioactive isotope decays into its daughter product is constant. This rate, however, varies considerably among different radioactive isotopes. Further, many radioactive isotopes undergo a series of transformations--some of which have half-lives that persist for only very short amounts of time--before they are converted into their final daughter products.
Below are some of the decay series that are commonly used in radiometric dating of geological samples. Note the great variations in their half-lives.
Absolute Age: Definition & Dating | arraya.co
Note that the half-life for the rubidium to strontium series is 50 billion years! Since the entire universe is At the other end of the spectrum, note the very short half-life of carbon The is the isotope that is used in "carbon dating. Both it and carbon which is stable, meaning that it does not undergo radioactive decay are incorporated into the tissues of plants as they grow. After a plant dies, the carbon in its tissues remains stable, but the carbon decays into nitrogen The ratio of carbon relative to carbon in a sample, therefore, may be used to determine the age of organic matter derived from plant tissues.
Because of its short half-life, carbon can only be used to date materials that are up to about 70, years old beyond this point, the amount of carbon remaining becomes so small that it is difficult to measure. Because of its precision, it is nevertheless very useful for dating organic matter from the near recent geological past, especially archeological materials from the Holocene epoch.
At the beginning of this chapter , you learned that the Earth is 4. As it turns out, the oldest dated mineral--a grain of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia--is 4. A single grain of zircon, imaged using a scanning electron microscope. A sample of 4. If the oldest mineral grain is 4. The answer is radiometric dating of meteorite specimens, which we presume to have formed around the same time as the Earth, Sun, and other planetary bodies in our solar system.