Prior to the best and most accepted age of the Earth was that proposed by Lord Kelvin based on the amount of time necessary for the.
Table of contents
Since we know that the , and assuming that the Pb and Pb dates are the same, then equation 11 is the equation for a family of lines that have a slope. The answer is about 6 billion years.
- Radioactive Dating;
- 18 year old daughter dating dad.
- dating for overweight guys.
- shim hyung tak dating.
- gentlemans guide to online dating download.
This argument tells when the elements were formed that make up the Earth, but does not really give us the age of the Earth. It does, however, give a maximum age of the Earth. Is this the age of the Earth? Lunar rocks also lie on the Geochron, at least suggesting that the moon formed at the same time as meteorites. Modern Oceanic Pb - i. Pb separated from continents and thus from average crust also plots on the Geochron, and thus suggests that the Earth formed at the same time as the meteorites and moon.
Thus, our best estimate of the age of the Earth is 4. The initial ratio has particular importance for studying the chemical evolution of the Earth's mantle and crust, as we discussed in the section on igneous rocks. Since K is one of the 10 most abundant elements in the Earth's crust, the decay of 40 K is important in dating rocks. But this scheme is not used because 40 Ca can be present as both radiogenic and non-radiogenic Ca.
Since Ar is a noble gas, it can escape from a magma or liquid easily, and it is thus assumed that no 40 Ar is present initially. Note that this is not always true. If a magma cools quickly on the surface of the Earth, some of the Ar may be trapped. If this happens, then the date obtained will be older than the date at which the magma erupted. For example lavas dated by K-Ar that are historic in age, usually show 1 to 2 my old ages due to trapped Ar.
Such trapped Ar is not problematical when the age of the rock is in hundreds of millions of years.
The dating equation used for K-Ar is: Some of the problems associated with K-Ar dating are Excess argon. This is only a problem when dating very young rocks or in dating whole rocks instead of mineral separates. Minerals should not contain any excess Ar because Ar should not enter the crystal structure of a mineral when it crystallizes.
Thus, it always better to date minerals that have high K contents, such as sanidine or biotite. If these are not present, Plagioclase or hornblende. If none of these are present, then the only alternative is to date whole rocks. Some 40 Ar could be absorbed onto the sample surface. This can be corrected for. Most minerals will lose Ar on heating above o C - thus metamorphism can cause a loss of Ar or a partial loss of Ar which will reset the atomic clock.
If only partial loss of Ar occurs then the age determined will be in between the age of crystallization and the age of metamorphism. If complete loss of Ar occurs during metamorphism, then the date is that of the metamorphic event. The problem is that there is no way of knowing whether or not partial or complete loss of Ar has occurred. Examples of questions on this material that could be asked on an exam.
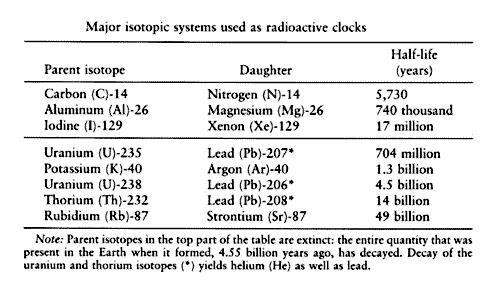
Prior to the best and most accepted age of the Earth was that proposed by Lord Kelvin based on the amount of time necessary for the Earth to cool to its present temperature from a completely liquid state. Principles of Radiometric Dating Radioactive decay is described in terms of the probability that a constituent particle of the nucleus of an atom will escape through the potential Energy barrier which bonds them to the nucleus. Thus, if we start out with 1 gram of the parent isotope, after the passage of 1 half-life there will be 0. Some examples of isotope systems used to date geologic materials.
Radiometric dating - Wikipedia
To see how we actually use this information to date rocks, consider the following: To account for this, we first note that there is an isotope of Sr, 86 Sr, that is: If we divide equation 4 through by the amount of 86 Sr, then we get: Note also that equation 5 has the form of a linear equation, i. How can we use this? Isotopic systems that have been exploited for radiometric dating have half-lives ranging from only about 10 years e. For most radioactive nuclides, the half-life depends solely on nuclear properties and is essentially a constant.
It is not affected by external factors such as temperature , pressure , chemical environment, or presence of a magnetic or electric field. For all other nuclides, the proportion of the original nuclide to its decay products changes in a predictable way as the original nuclide decays over time. This predictability allows the relative abundances of related nuclides to be used as a clock to measure the time from the incorporation of the original nuclides into a material to the present.
The basic equation of radiometric dating requires that neither the parent nuclide nor the daughter product can enter or leave the material after its formation. The possible confounding effects of contamination of parent and daughter isotopes have to be considered, as do the effects of any loss or gain of such isotopes since the sample was created. It is therefore essential to have as much information as possible about the material being dated and to check for possible signs of alteration. Alternatively, if several different minerals can be dated from the same sample and are assumed to be formed by the same event and were in equilibrium with the reservoir when they formed, they should form an isochron.
This can reduce the problem of contamination. In uranium—lead dating , the concordia diagram is used which also decreases the problem of nuclide loss.
Finally, correlation between different isotopic dating methods may be required to confirm the age of a sample. For example, the age of the Amitsoq gneisses from western Greenland was determined to be 3. Accurate radiometric dating generally requires that the parent has a long enough half-life that it will be present in significant amounts at the time of measurement except as described below under "Dating with short-lived extinct radionuclides" , the half-life of the parent is accurately known, and enough of the daughter product is produced to be accurately measured and distinguished from the initial amount of the daughter present in the material.
The procedures used to isolate and analyze the parent and daughter nuclides must be precise and accurate. This normally involves isotope-ratio mass spectrometry. The precision of a dating method depends in part on the half-life of the radioactive isotope involved. For instance, carbon has a half-life of 5, years.
K-Ar dating calculation
After an organism has been dead for 60, years, so little carbon is left that accurate dating cannot be established. On the other hand, the concentration of carbon falls off so steeply that the age of relatively young remains can be determined precisely to within a few decades. If a material that selectively rejects the daughter nuclide is heated, any daughter nuclides that have been accumulated over time will be lost through diffusion , setting the isotopic "clock" to zero.
The temperature at which this happens is known as the closure temperature or blocking temperature and is specific to a particular material and isotopic system. These temperatures are experimentally determined in the lab by artificially resetting sample minerals using a high-temperature furnace. As the mineral cools, the crystal structure begins to form and diffusion of isotopes is less easy. At a certain temperature, the crystal structure has formed sufficiently to prevent diffusion of isotopes.
This temperature is what is known as closure temperature and represents the temperature below which the mineral is a closed system to isotopes. Thus an igneous or metamorphic rock or melt, which is slowly cooling, does not begin to exhibit measurable radioactive decay until it cools below the closure temperature. The age that can be calculated by radiometric dating is thus the time at which the rock or mineral cooled to closure temperature.
This field is known as thermochronology or thermochronometry. The mathematical expression that relates radioactive decay to geologic time is [12] [15]. The equation is most conveniently expressed in terms of the measured quantity N t rather than the constant initial value N o.
- welders dating.
- Radiometric dating.
- daughter dating loser boyfriend.
- hook up pin in dft.
- sarah eden dating.
- best mobile dating app 2015.
- ;
The above equation makes use of information on the composition of parent and daughter isotopes at the time the material being tested cooled below its closure temperature. This is well-established for most isotopic systems. Plotting an isochron is used to solve the age equation graphically and calculate the age of the sample and the original composition.
Radiometric dating has been carried out since when it was invented by Ernest Rutherford as a method by which one might determine the age of the Earth. In the century since then the techniques have been greatly improved and expanded. The mass spectrometer was invented in the s and began to be used in radiometric dating in the s. It operates by generating a beam of ionized atoms from the sample under test.
Radiometric dating
The ions then travel through a magnetic field, which diverts them into different sampling sensors, known as " Faraday cups ", depending on their mass and level of ionization. On impact in the cups, the ions set up a very weak current that can be measured to determine the rate of impacts and the relative concentrations of different atoms in the beams. Uranium—lead radiometric dating involves using uranium or uranium to date a substance's absolute age. This scheme has been refined to the point that the error margin in dates of rocks can be as low as less than two million years in two-and-a-half billion years.
Uranium—lead dating is often performed on the mineral zircon ZrSiO 4 , though it can be used on other materials, such as baddeleyite , as well as monazite see: Zircon has a very high closure temperature, is resistant to mechanical weathering and is very chemically inert.
Navigation menu
Zircon also forms multiple crystal layers during metamorphic events, which each may record an isotopic age of the event. One of its great advantages is that any sample provides two clocks, one based on uranium's decay to lead with a half-life of about million years, and one based on uranium's decay to lead with a half-life of about 4.
This can be seen in the concordia diagram, where the samples plot along an errorchron straight line which intersects the concordia curve at the age of the sample. This involves the alpha decay of Sm to Nd with a half-life of 1. Accuracy levels of within twenty million years in ages of two-and-a-half billion years are achievable. This involves electron capture or positron decay of potassium to argon Potassium has a half-life of 1.