Relative dating is used to arrange geological events, and the rocks they within the Mesozoic, so identifying a fossil species can help narrow.
Table of contents
- Relative Vs. Absolute Dating: The Ultimate Face-off
- Relative Vs. Absolute Dating: The Ultimate Face-off
- Navigation menu
The layers are horizontally placed. Thus, it follows the principle of horizontality. While some of the layers are uplifted, most of the landform is left undisturbed by nature. It is the evidence of Earth's history over such a long span of time. It is a perfect example of superposition layers deposited one above the other and lateral continuity undisturbed and covering large distances. Relative Dating Techniques in Geology.
Geology refers to the study of the rocks and sediments that to a great extent compose the Earth. This oldest relative dating technique in the branch of geology, as the name suggests, focuses mainly on the strata. It concentrates mainly on the placement of the strata as well as its chronological sequence. The principle of superposition is the core principle used in this method. Strata is the layered arrangement or soil or rocks which lie parallel, one above the other.
Each layer has a unique layer and consists of different sediments or material.
The principle of superposition states that the layer which lies at the bottom is older than the one on top of it. In stratigraphic relative dating, the succession of layers can be seen as the timeline of its formation or deposition. However, this is mainly applicable to an undisturbed arrangement of rocks. Most of the rock arrangements are disturbed by natural forces, such as wind and water, which result in unconformity in the sequence of rocks.
Relative Vs. Absolute Dating: The Ultimate Face-off
Layers get deposited above one another, over time, and fossils get trapped in these layers. When we find two fossils in the same strata of soil, we assume that both fossils were deposited during the same time period. If an animal fossil is found, and the time during which it lived is known, it helps us understand the time period of any other fossil found in the same strata. Animals evolve rapidly, and these evolution's are reflected by the variations in their bones or teeth.
Relative Vs. Absolute Dating: The Ultimate Face-off
When they die, their remains get fossilized and are used by scientists to determine the era in which they lived. These fossils are then used as standards to determine the age of other fossils.
They are called 'Index fossils'. An example can be fossils of some species of monkeys found alongside fossils of human species. This technique of relative dating mainly works on the principle of chemical changes taking place in the fossils. When remains of living beings get buried into sediments and turn to fossils, the bacteria present in the soil breakdown the proteins and fats from the bones.
Most of the nitrogen contained in these fossils gets depleted progressively. Ground water percolates into these rocks and deposits its component elements such as fluorine, uranium, etc. The amount of fluorine in the fossils thus increases. If two fossils belong to the same strata, then they are assumed to have the same amount of nitrogen and fluorine. In case of a difference in the fluorine content, they are considered to be from different eras.
Relative Dating Technique in Anthropology. This is because inclusions can act like "fossils" — trapping and preserving these early melts before they are modified by later igneous processes. In addition, because they are trapped at high pressures many melt inclusions also provide important information about the contents of volatile elements such as H 2 O, CO 2 , S and Cl that drive explosive volcanic eruptions. Sorby was the first to document microscopic melt inclusions in crystals.
The study of melt inclusions has been driven more recently by the development of sophisticated chemical analysis techniques. Scientists from the former Soviet Union lead the study of melt inclusions in the decades after World War II Sobolev and Kostyuk, , and developed methods for heating melt inclusions under a microscope, so changes could be directly observed.
Although they are small, melt inclusions may contain a number of different constituents, including glass which represents magma that has been quenched by rapid cooling , small crystals and a separate vapour-rich bubble. They occur in most of the crystals found in igneous rocks and are common in the minerals quartz , feldspar , olivine and pyroxene. The formation of melt inclusions appears to be a normal part of the crystallization of minerals within magmas, and they can be found in both volcanic and plutonic rocks.
The law of included fragments is a method of relative dating in geology. Essentially, this law states that clasts in a rock are older than the rock itself. Another example is a derived fossil , which is a fossil that has been eroded from an older bed and redeposited into a younger one. This is a restatement of Charles Lyell 's original principle of inclusions and components from his to multi-volume Principles of Geology , which states that, with sedimentary rocks , if inclusions or clasts are found in a formation , then the inclusions must be older than the formation that contains them.
These foreign bodies are picked up as magma or lava flows , and are incorporated, later to cool in the matrix. As a result, xenoliths are older than the rock which contains them Relative dating is used to determine the order of events on Solar System objects other than Earth; for decades, planetary scientists have used it to decipher the development of bodies in the Solar System , particularly in the vast majority of cases for which we have no surface samples.
Many of the same principles are applied.
- Relative dating - Wikipedia?
- indian dating apps download?
- Types of relative dating?
- isle of man dating?
- 2 types of relative dating - Murmuration?
For example, if a valley is formed inside an impact crater , the valley must be younger than the crater. Craters are very useful in relative dating; as a general rule, the younger a planetary surface is, the fewer craters it has. If long-term cratering rates are known to enough precision, crude absolute dates can be applied based on craters alone; however, cratering rates outside the Earth-Moon system are poorly known.
Relative dating methods in archaeology are similar to some of those applied in geology. The principles of typology can be compared to the biostratigraphic approach in geology. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. For relative dating of words and sounds in languages, see Historical linguistics.
Dating methodologies in archaeology. EJ Brill , The earth through time 9th ed. Dinosaurs and the History of Life. HarperCollins, , pp. Canon of Kings Lists of kings Limmu.
Navigation menu
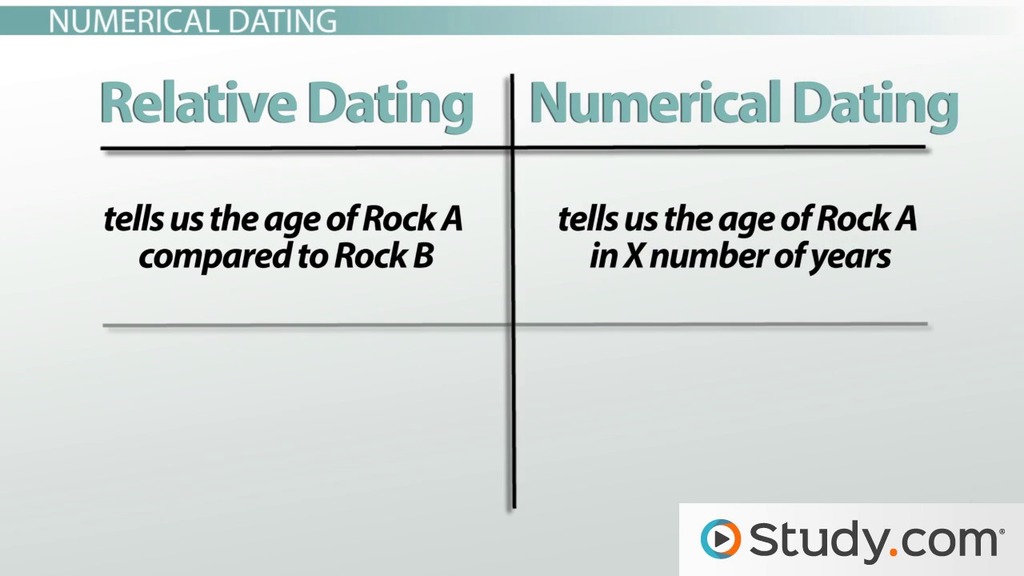
Chinese Japanese Korean Vietnamese. Lunisolar Solar Lunar Astronomical year numbering. To find their age, two major geological dating methods are used. These are called relative and absolute dating techniques. Absolute dating, also called numerical dating, arranges the historical remains in order of their ages. Whereas, relative dating arranges them in the geological order of their formation.
- ?
- does asap rocky dating rihanna?
- online dating texting examples?
- dating blueprint?
The relative dating techniques are very effective when it comes to radioactive isotope or radiocarbon dating. However, not all fossils or remains contain such elements. Relative techniques are of great help in such types of sediments. The following are the major methods of relative dating. The oldest dating method which studies the successive placement of layers. It is based on the concept that the lowest layer is the oldest and the topmost layer is the youngest. An extended version of stratigraphy where the faunal deposits are used to establish dating. Faunal deposits include remains and fossils of dead animals.
This method compares the age of remains or fossils found in a layer with the ones found in other layers.
- Relative Dating: Applications and Important Techniques Explained?
- best dating sites guide?
- Relative Dating?
The comparison helps establish the relative age of these remains. Bones from fossils absorb fluorine from the groundwater. The amount of fluorine absorbed indicates how long the fossil has been buried in the sediments.